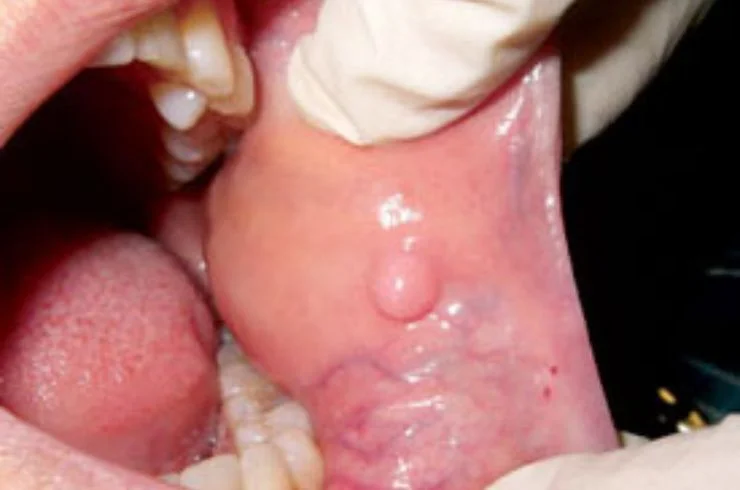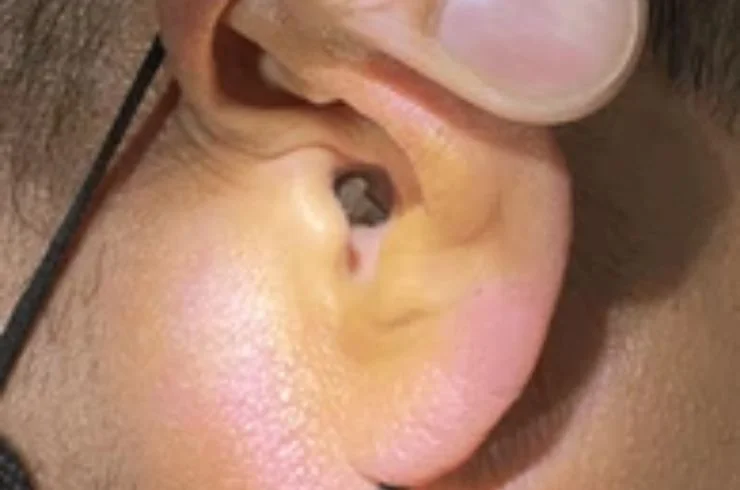
Foreign body removal from the ear, nose, or throat is a common ENT procedure performed to safely extract objects that may accidentally enter these areas. Foreign bodies can include small items like beads, seeds, insects, or food particles, often seen in children or adults. Symptoms vary depending on the location and may include pain, discomfort, swelling, breathing difficulties, or hearing impairment. Specialized instruments like forceps, suction devices, or endoscopes are used to remove the object without causing damage. Prompt removal is crucial to prevent complications like infections, tissue damage, or blockages. This procedure is typically quick and performed under local anesthesia, ensuring minimal discomfort and a speedy recovery. Always seek professional help for safe and effective removal.
Endoscopy for the ear, nose, and throat is a minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that allows detailed visualization of the ENT structures. Using a thin, flexible tube equipped with a light and camera (endoscope), specialists can examine areas like the nasal passages, sinuses, throat, and ear canals. This procedure is commonly performed to evaluate conditions such as nasal obstructions, sinus infections, voice disorders, ear blockages, and throat pain. It aids in diagnosing issues like polyps, tumors, or structural abnormalities. ENT endoscopy is typically performed in a clinical setting with minimal discomfort and no downtime. In some cases, it can also assist in minor surgical procedures. This advanced approach ensures accurate diagnosis and effective treatment planning, improving patient outcomes.
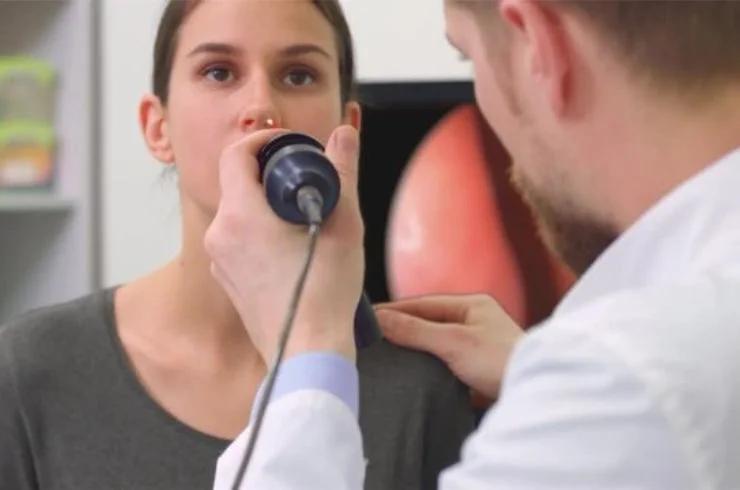
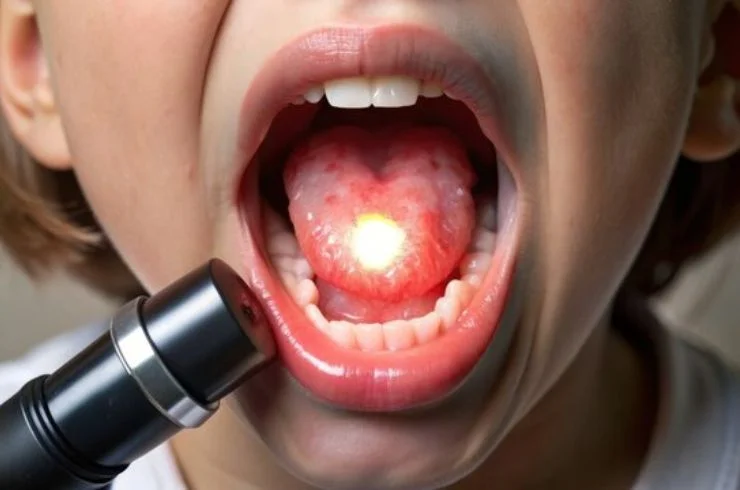
Tonsillectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the tonsils, which are lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. It is commonly performed to treat recurrent tonsillitis, chronic sore throat, sleep apnea, or enlarged tonsils causing breathing or swallowing difficulties. The surgery is conducted under general anesthesia, using advanced techniques like cold steel dissection, cauterization, or laser to ensure precision and minimize bleeding. Recovery typically involves a few days of rest, with some throat discomfort and dietary adjustments. Tonsillectomy significantly improves quality of life by reducing infections, improving breathing, and alleviating symptoms associated with tonsillar problems. It is a safe and effective solution for individuals with persistent throat issues unresponsive to conservative treatments.
Septoplasty combined with Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS) is a dual surgical approach to address nasal obstructions and chronic sinus issues. Septoplasty corrects a deviated nasal septum by repositioning and straightening the cartilage and bone, enhancing airflow and resolving breathing difficulties. FESS focuses on clearing blocked sinuses using minimally invasive endoscopic techniques to remove obstructions, polyps, or infected tissue, restoring normal sinus drainage. This combined procedure is often performed under general anesthesia and is ideal for patients with nasal blockage, recurrent sinus infections, or sinus-related headaches. Post-surgery, patients experience improved breathing, reduced sinus infections, and overall enhanced quality of life. Recovery involves mild swelling or congestion, with full benefits typically visible within a few weeks.
Tympanoplasty is a surgical procedure to repair a perforated eardrum (tympanic membrane) or reconstruct the small bones of the middle ear to restore hearing and prevent recurrent ear infections. It is commonly performed for patients with chronic ear infections, trauma-induced eardrum perforation, or conductive hearing loss. The procedure involves grafting tissue to close the eardrum hole, and in some cases, reconstructing damaged ossicles. Tympanoplasty is typically done under general or local anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition. Post-surgery, patients may experience mild discomfort or dizziness, with recovery spanning a few weeks. This effective surgery significantly improves hearing, reduces infections, and enhances the overall quality of life for individuals with chronic ear issues.
Cortical mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure performed to treat infections or conditions affecting the mastoid bone, located behind the ear. This bone contains air cells connected to the middle ear, and infections such as mastoiditis can spread into these spaces. The procedure involves removing the diseased mastoid air cells to eliminate infection, prevent complications, and restore ear health. It is often performed alongside other surgeries like tympanoplasty to address middle ear issues. Conducted under general anesthesia, cortical mastoidectomy involves minimal discomfort post-surgery, with recovery typically lasting a few weeks. This surgery is essential for treating chronic ear infections and preventing complications such as hearing loss or intracranial infections, significantly improving the patient’s ear health and overall well-being.

Modified radical mastoidectomy is a surgical procedure designed to treat chronic ear infections or cholesteatoma (abnormal skin growth in the middle ear) by removing infected tissue from the middle ear and mastoid bone. Unlike a radical mastoidectomy, which completely removes the structures in the middle ear, a modified version aims to preserve the hearing structures as much as possible. The procedure involves removing diseased mastoid air cells and cleaning the ear to prevent recurrent infections, while the eardrum and ossicles may be preserved or reconstructed. This surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia and helps prevent the spread of infections, improve ear health, and restore hearing in many cases. Post-surgery recovery may involve a few weeks of rest, with some swelling or discomfort, but it significantly improves quality of life by resolving chronic ear issues.
An oral biopsy is a medical procedure used to remove a small sample of tissue from the mouth to diagnose potential oral conditions, such as oral cancer, infections, or other abnormalities. The tissue sample is sent to a laboratory for microscopic examination to identify the presence of diseases or infections. Oral biopsies are typically performed when a patient presents with unusual lesions, growths, or persistent sores that do not heal. The procedure is usually done under local anesthesia to numb the area, and it can be performed using different techniques, such as incisional (removing part of the tissue) or excisional (removing the entire lesion). Recovery involves minimal discomfort, and the results of the biopsy can provide essential information to guide treatment options, ensuring timely intervention for any underlying conditions.