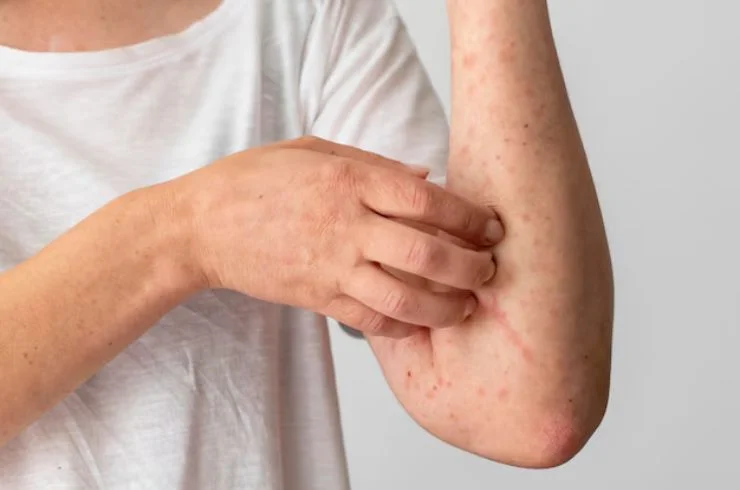
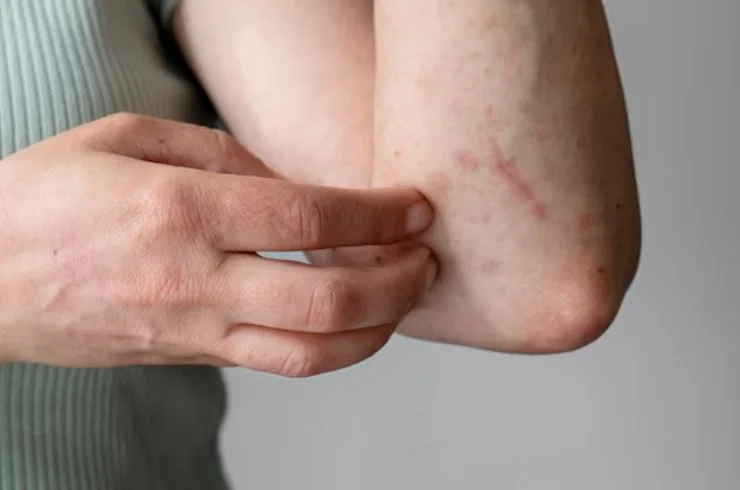
Rashes are common skin conditions characterized by redness, irritation, and itching, often caused by allergies, infections, or underlying health issues like eczema or psoriasis. Environmental factors such as heat, certain fabrics, or harsh chemicals can also trigger rashes. Common types include hives, fungal infections, viral rashes, and allergic reactions. Treatment depends on the rash’s cause and severity, including topical creams, oral medications, or lifestyle changes to avoid triggers. In cases of persistent or severe rashes, seeking professional medical advice is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Early intervention helps relieve discomfort, prevent further skin damage, and manage symptoms. If over-the-counter remedies aren’t effective, consulting a dermatologist ensures targeted care for faster recovery and healthier skin.
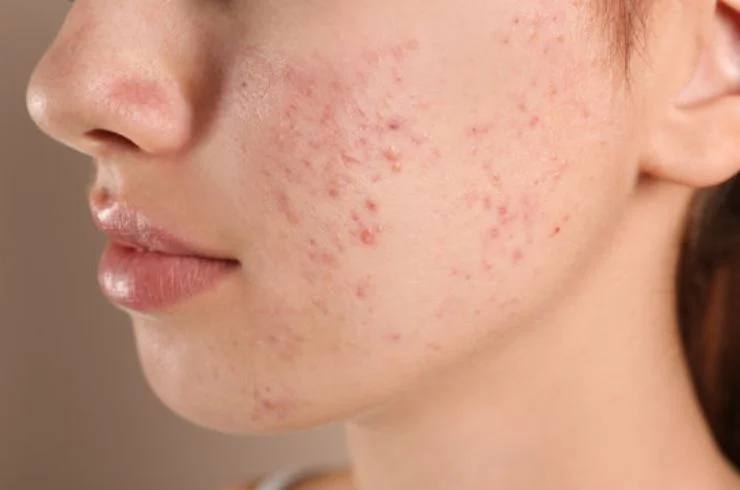
Acne, commonly known as pimples, is a skin condition that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria. This can lead to the formation of pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts. Acne often affects the face, back, shoulders, and chest, and is most common during puberty but can occur at any age. Factors such as hormonal changes, stress, poor diet, and using harsh skincare products can trigger or worsen acne. Treatment options include topical creams, oral medications, and lifestyle changes like maintaining a consistent skincare routine and a balanced diet. Severe acne may require professional treatments such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or extractions. Managing acne early can prevent scarring and improve skin appearance. If you’re struggling with acne, a dermatologist can help determine the best treatment plan tailored to your skin’s needs.
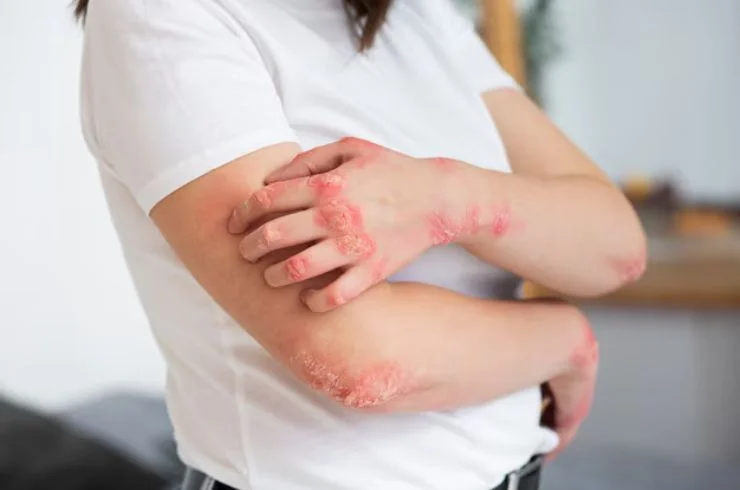


Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that causes skin cells to grow too quickly, leading to thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. These patches commonly appear on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back but can develop anywhere on the body. Psoriasis is often triggered by factors such as stress, infections, weather changes, and certain medications. Symptoms include itching, burning, and discomfort. While there is no cure for psoriasis, effective treatments are available to manage the condition and reduce flare-ups. Topical treatments like corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and moisturizers can help control mild psoriasis. In more severe cases, phototherapy or systemic medications may be required. With proper treatment, psoriasis can be controlled, improving skin appearance and quality of life. Consulting a dermatologist is essential to develop a personalized treatment plan to manage psoriasis effectively and prevent flare-ups.
Skin allergies occur when the immune system reacts to a substance that comes into contact with the skin, causing redness, itching, swelling, and sometimes blisters. Common allergens include certain foods, plants, cosmetics, detergents, metals (like nickel), and insect stings. Conditions like eczema, contact dermatitis, and hives are often linked to skin allergies. The symptoms of skin allergies can range from mild irritation to severe reactions and may require medical intervention. Treatment typically involves identifying and avoiding the allergen, using antihistamines, corticosteroid creams, or moisturizers to soothe the skin. In more severe cases, oral medications or allergy shots may be recommended. A dermatologist can help diagnose the underlying cause of your skin allergy and create a personalized treatment plan to manage symptoms effectively, reduce flare-ups, and maintain healthy skin.
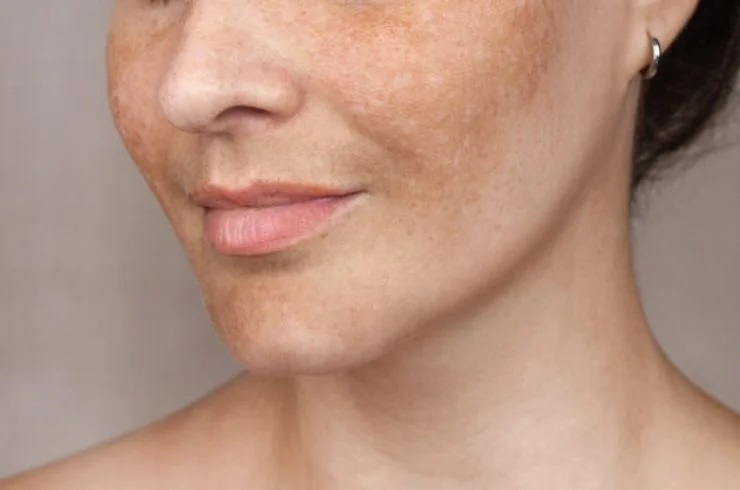
Pigmentary disorders refer to changes in the skin’s color, often resulting from excess or insufficient melanin production. Common types include suntan, melasma, and freckles, each with distinct causes and treatments.
Suntan: Caused by prolonged exposure to sunlight, suntan occurs when the skin produces more melanin to protect itself from UV rays. While it fades naturally over time, sunscreen and skin care treatments can help speed up the process and prevent future tanning.
Melasma: Characterized by dark patches on the face, melasma is often triggered by hormonal changes during pregnancy, birth control use, or sun exposure. Treatment options include topical treatments like hydroquinone, chemical peels, and laser therapy.
Freckles: These small, brown spots are genetic and usually appear on sun-exposed areas. Though harmless, they can be lightened with topical treatments, sunscreens, and laser therapy.
Skin infections can be caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses, each requiring specific treatments.
Bacterial Infections: These infections, such as impetigo or cellulitis, occur when harmful bacteria invade the skin. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and pus. Antibiotics, either topical or oral, are commonly used to treat bacterial skin infections.
Fungal Infections: Fungal infections like ringworm, athlete’s foot, and candidiasis thrive in warm, moist environments. Antifungal creams, lotions, or oral medications can effectively treat these infections.
Viral Infections: Viral infections like warts (caused by the HPV virus) and herpes (caused by the herpes simplex virus) lead to painful blisters or growths. Antiviral treatments and in some cases, cryotherapy or laser treatments, can manage these conditions.
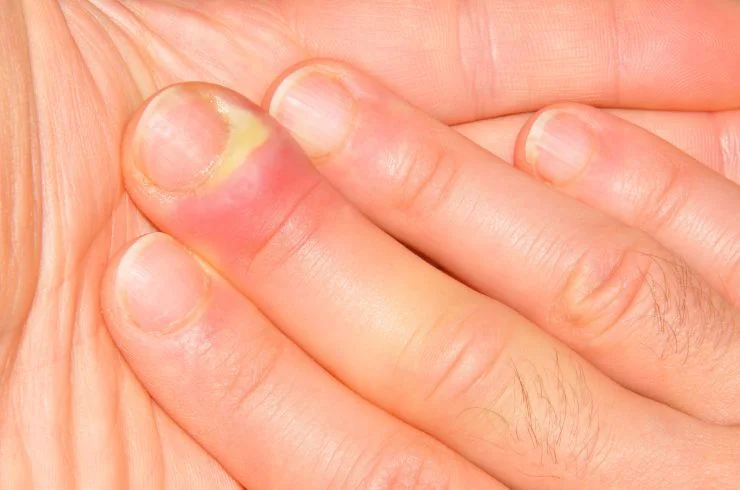
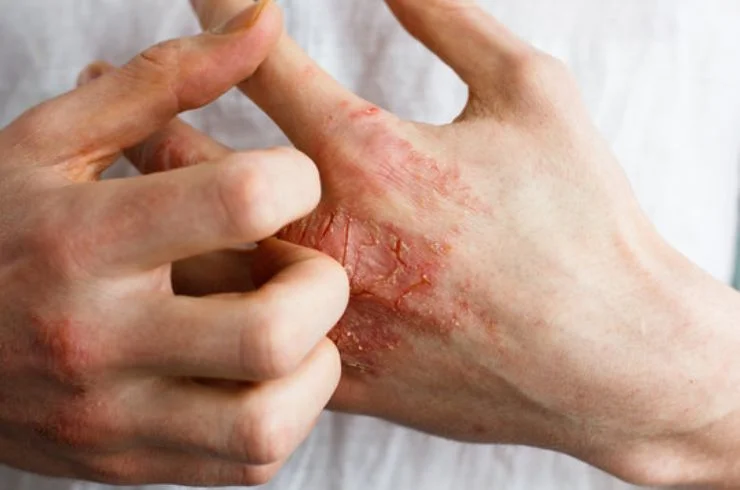
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, redness, itching, and dryness. It occurs when the skin’s barrier is weakened, leading to increased sensitivity to environmental factors like allergens, irritants, and stress. Eczema can affect people of all ages and often appears on the face, hands, elbows, and knees. The exact cause is unknown, but it is thought to be related to a combination of genetics and immune system dysfunction. Treatment for eczema typically involves moisturizing the skin, using topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and avoiding triggers that worsen symptoms. In some cases, antihistamines, phototherapy, or immunosuppressive medications may be recommended. With proper care and management, eczema can be controlled, reducing flare-ups and improving the quality of life. A dermatologist can help develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Atopic dermatitis, also known as atopic derma, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes redness, itching, and dryness. It is often linked to other allergic conditions such as asthma and hay fever. This condition is caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors that weaken the skin’s protective barrier, leading to increased sensitivity to irritants and allergens. Common symptoms include dry, scaly patches, intense itching, and skin inflammation. Treatment usually involves moisturizing the skin regularly, using topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and avoiding triggers such as allergens, soaps, or extreme weather conditions. In more severe cases, other treatments like topical calcineurin inhibitors, phototherapy, or oral medications may be prescribed. Managing atopic dermatitis requires consistent care and lifestyle modifications to prevent flare-ups and improve skin health. A dermatologist can provide personalized treatment and advice for effective management.
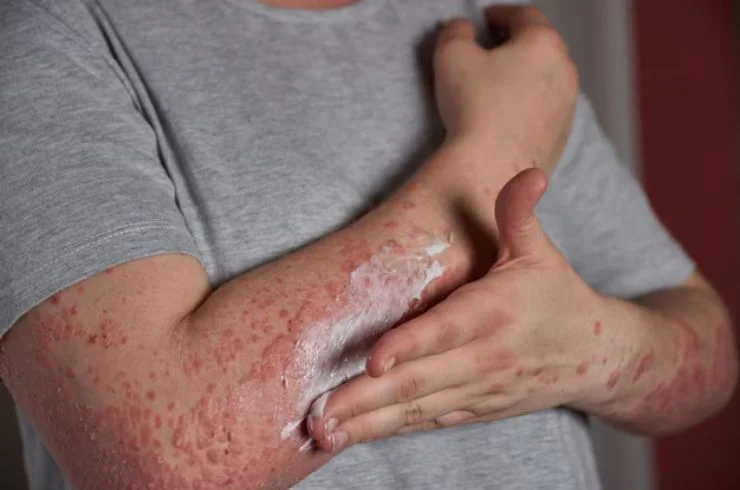
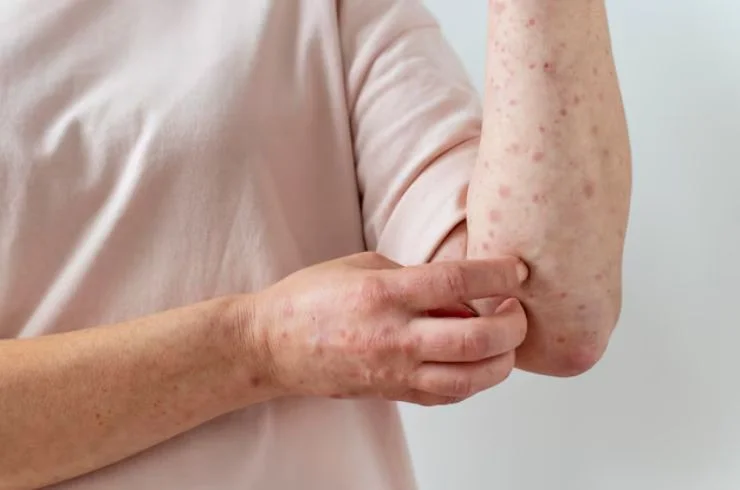
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by raised, red, itchy welts or bumps on the skin. These welts can vary in size and often appear suddenly. Urticaria is usually caused by an allergic reaction to foods, medications, insect stings, or environmental factors like heat, stress, or temperature changes. It can also result from certain infections or underlying health conditions. The primary symptom of urticaria is intense itching, and the rash typically lasts for a few hours but can recur. Treatment typically involves antihistamines to relieve itching and reduce the size of the welts. In severe cases, corticosteroids or other medications may be prescribed to control inflammation. Identifying and avoiding triggers is essential in preventing flare-ups. If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment to manage the condition effectively.
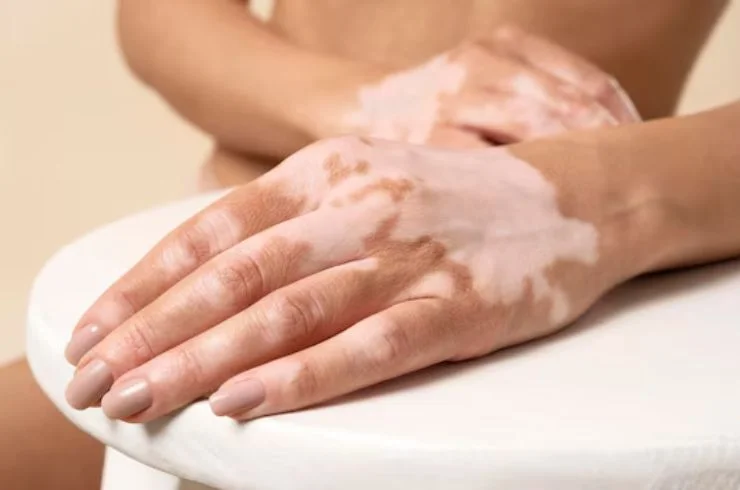
Vitiligo is a skin condition characterized by the loss of pigment, leading to white patches on the skin. It occurs when melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing skin color, are destroyed or malfunction. The exact cause is unclear, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy pigment cells. Vitiligo can affect any area of the body, including the face, hands, and genital region. While there is no cure, treatments aim to slow the progression and restore skin color. Options include topical corticosteroids, light therapy, and skin grafting. In some cases, cosmetic options like makeup or self-tanners may help camouflage the patches. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and improve appearance. A dermatologist can help tailor a treatment plan specific to your condition.

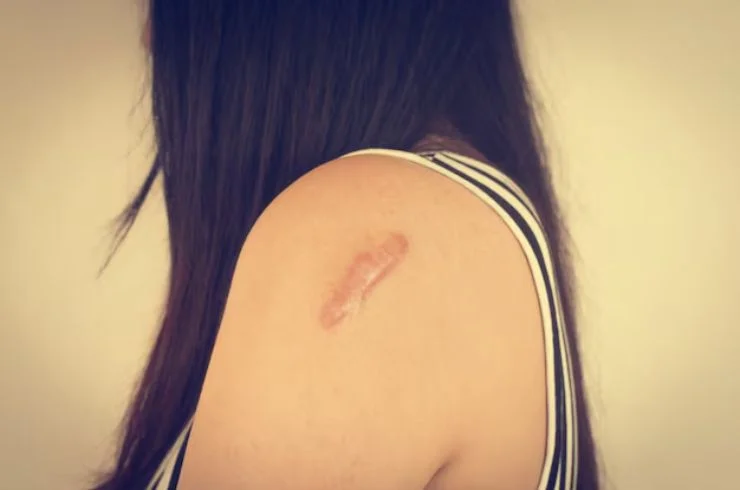
Scars form as part of the natural healing process after skin injury, surgery, or inflammation, often fading over time but sometimes remaining visible. Treatments like silicone gels, corticosteroid creams, and laser therapy can help improve the appearance of scars. Keloids, on the other hand, are thick, raised scars that extend beyond the original injury site due to excessive collagen production. These can be more prominent and may require more intensive treatments, such as corticosteroid injections, cryotherapy, laser therapy, or even surgical removal. Although keloids can be persistent and may recur, timely and targeted interventions can significantly reduce their size and enhance skin appearance. A dermatologist can evaluate and recommend the most suitable treatment for both scars and keloids, helping you achieve smoother, healthier-looking skin.
Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer and occurs when skin cells grow abnormally. It is often caused by excessive sun exposure and UV radiation, which damage the DNA in skin cells. The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are often localized and treatable, while melanoma can be more aggressive and spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms may include unusual moles, changes in existing moles, or new growths on the skin. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Treatment options include surgical excision, cryotherapy, topical medications, and in some cases, radiation or chemotherapy. Regular skin checks and sun protection are essential in preventing skin cancer. A dermatologist can provide personalized care and advice for prevention and treatment.
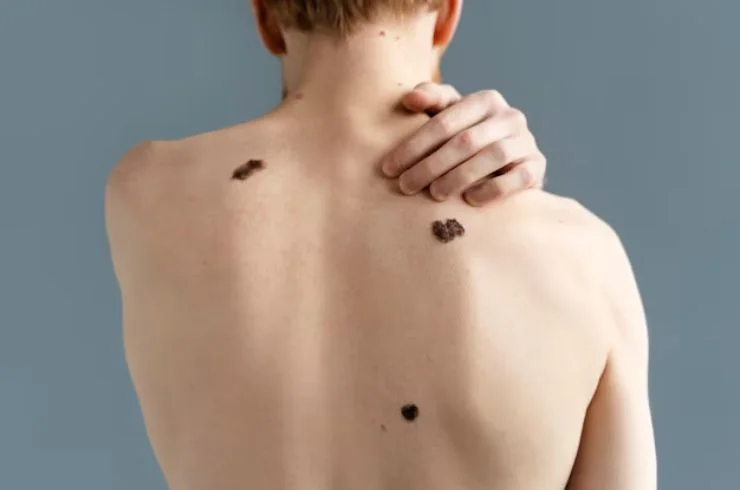
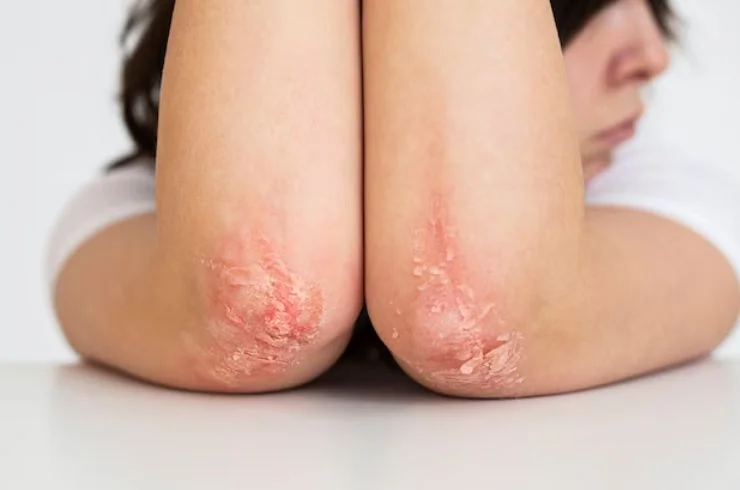
Skin ulcers are open sores or lesions that can form due to a variety of causes, including poor circulation, infections, pressure, or underlying health conditions like diabetes or venous insufficiency. These ulcers can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the legs or feet. Symptoms include pain, swelling, redness, and in some cases, a discharge. Treatment for skin ulcers typically focuses on healing the wound, addressing the underlying cause, and preventing infection. This may involve cleaning the ulcer, applying topical treatments like antibiotics or antiseptics, and using dressings to promote healing. In cases of chronic ulcers, advanced treatments like wound debridement, compression therapy, or even surgical intervention may be required. Managing conditions such as diabetes or vascular issues is crucial to prevent recurrence. A dermatologist or healthcare provider can offer personalized treatment plans for optimal healing.
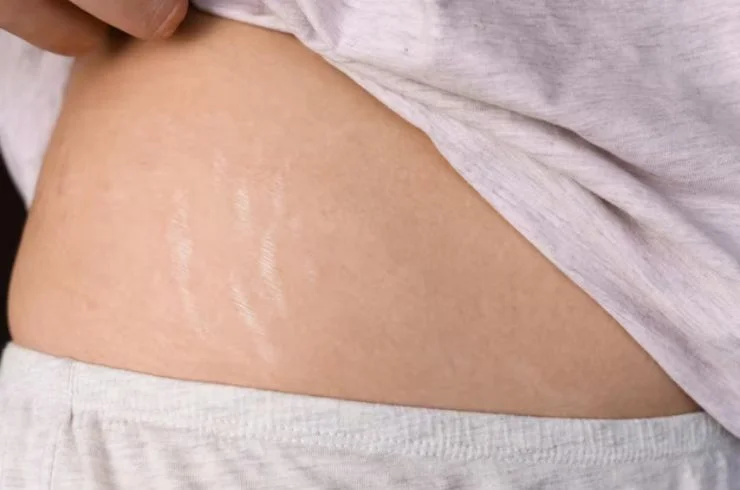
Stretch marks, or striae, are common skin marks that appear when the skin is stretched rapidly due to growth spurts, pregnancy, weight gain, or hormonal changes. These marks typically begin as red, purple, or dark streaks and fade to a lighter color over time. While stretch marks are harmless, they can be a cosmetic concern. Treatment options to improve their appearance include topical creams with ingredients like retinoids, hyaluronic acid, and vitamin E, which may promote collagen production and skin regeneration. Laser therapy, microdermabrasion, and chemical peels are also effective in reducing stretch mark visibility. Although treatments can help minimize the appearance of stretch marks, they may not completely eliminate them. Early intervention tends to yield the best results. A dermatologist can recommend a treatment plan based on the severity and location of stretch marks.

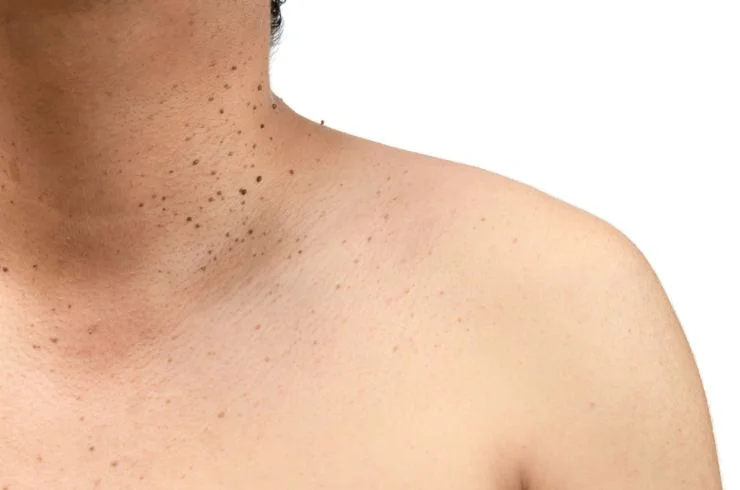
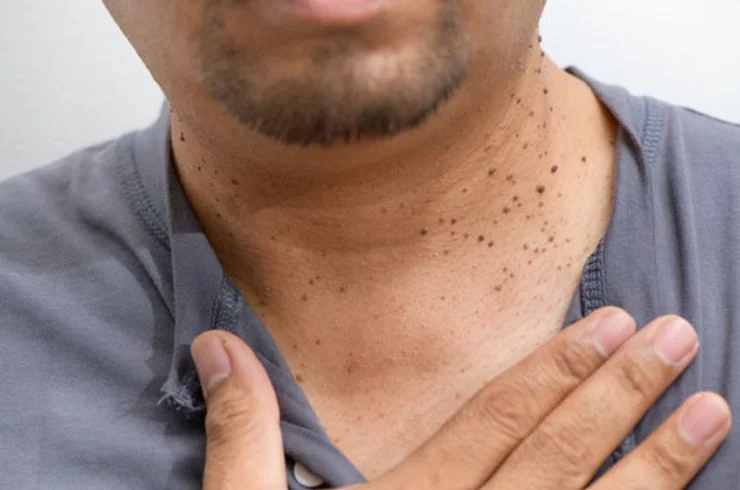
Dermatosis papulosa nigra (DPN) refers to small, dark, benign growths that commonly appear on the face, neck, and upper chest, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones. These papules are typically harmless and result from the overgrowth of melanocytes (pigment-producing cells). DPNs often become more noticeable with age and can vary in size and number. While they do not pose any health risks, many people seek treatment for cosmetic reasons. The most effective treatments for DPNs include cryotherapy (freezing), laser therapy, or electrosurgery, which remove or reduce the appearance of these spots. It’s important to consult a dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment and to ensure proper care to avoid scarring or complications. Regular monitoring is advised to distinguish DPNs from other skin conditions.
Skin tags are small, soft, benign growths of skin that often appear in areas where skin rubs against skin or clothing, such as the neck, armpits, groin, or eyelids. They are usually flesh-colored or slightly darker and can range in size. While skin tags are harmless and painless, they can be a cosmetic concern or cause discomfort if irritated by friction. Treatment options include removal through methods such as cryotherapy (freezing), excision (cutting), or electrocautery (burning). These procedures are quick, minimally invasive, and typically result in minimal scarring. While skin tags do not typically recur once removed, new ones may develop over time. It’s important to consult with a dermatologist to ensure accurate diagnosis and safe removal of skin tags, as other skin conditions can mimic their appearance.